In the dynamic landscape of small business ventures, establishing a robust sales process is paramount to sustained growth and profitability. This article delves into the intricacies of creating a winning sales process tailored specifically for small businesses and business owners.
From identifying target customers and qualifying leads to closing deals and continuous improvement, each aspect plays a pivotal role in driving sales success.
Understanding the Importance of a Sales Process for Small Businesses

In the realm of small businesses, having a well-defined sales process for a small business is not just a luxury but a necessity for sustained growth and success. Here’s why understanding and implementing a structured sales process is crucial:
Small businesses operate in dynamic environments where every sale matters. Without a clear sales process, businesses risk inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and inconsistent performance.
Sales activities are the lifeblood of any business, driving revenue generation and fostering customer relationships. A robust sales process ensures that these activities are organized, strategic, and result-oriented.
Companies that embrace a formal sales process experience higher productivity, better sales outcomes, and improved customer satisfaction. It’s not just about making sales but about doing so in a systematic and effective manner.
A well-defined sales process empowers small business owners and their sales teams with clarity, direction, and focus. It outlines the steps from prospecting to closing deals, guiding every interaction and decision along the way.
By establishing a sales process, small businesses can identify and capitalize on opportunities, adapt to market changes, and achieve sustainable growth. It becomes a roadmap for success, aligning sales efforts with overall business objectives.
Key components of an effective sales process for small businesses include:
- Prospect Identification: Identifying potential customers and qualifying them based on fit and interest.
- Sales Steps: Defining clear steps from initial contact to follow-ups, presentations, and negotiations.
- Product Knowledge: Equipping sales reps with in-depth knowledge of products or services to address customer needs effectively.
- CRM Integration: Leveraging Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools to manage sales data, track interactions, and nurture relationships.
- Team Collaboration: Fostering collaboration and alignment between sales teams and other departments to deliver seamless customer experiences.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating and refining the sales process based on performance metrics, feedback, and market trends.
Implementing a structured sales process is not just about ticking boxes but about creating a strategic framework that drives sales excellence and fuels business growth. It’s a journey of optimization, adaptation, and customer-centricity that small business owners must embark upon for long-term success.
Key Components of a Sales Process Flowchart
Visual representations are powerful tools for understanding complex processes. When it comes to sales, a sales process flowchart can be invaluable for small businesses. Here are the key components and benefits of creating a sales process flowchart:
- Visual Clarity: A sales process flowchart provides a clear, visual representation of the sales process from start to finish. It breaks down the steps into manageable chunks, making it easier for sales teams to follow and understand.
- Process Mapping: The flowchart maps out each stage of the sales cycle, including prospecting, qualifying leads, presentations, negotiations, and closing deals. This mapping helps small businesses identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement in their sales processes.
- Standardization: By standardizing the sales process through a flowchart, small businesses ensure consistency in sales activities across sales teams and individuals. This consistency leads to better predictability in sales outcomes and customer interactions.
- Training Tool: The flowchart serves as a valuable training tool for new sales reps. It allows them to visualize the entire sales process and understand their roles and responsibilities at each stage. This reduces ramp-up time and improves onboarding efficiency.
- Communication Aid: A sales process flowchart facilitates communication and collaboration among sales team members, managers, and other departments involved in the sales cycle. It ensures everyone is on the same page regarding sales strategies, priorities, and timelines.
- CRM Integration: Integrating the flowchart with a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system enhances its functionality. Small businesses can track sales progress, record customer interactions, and automate certain sales tasks based on the flowchart’s guidelines.
Creating a sales process flowchart involves several key steps:
- Define Process Steps: Identify and list down the steps involved in your sales process, from lead generation to deal closure.
- Sequence Steps: Arrange the steps in a logical sequence that reflects the actual flow of sales activities.
- Include Decision Points: Incorporate decision points where sales reps need to make choices or qualify leads based on criteria.
- Add Inputs and Outputs: Specify the inputs required at each stage (prospect information, product details) and the desired outputs (e.g., qualified leads, closed deals).
- Review and Refine: Review the flowchart with sales teams and stakeholders, gather feedback, and refine the flowchart as needed to improve clarity and effectiveness.
- Document and Distribute: Document the finalized sales process flowchart and distribute it to sales teams, ensuring everyone has access to the updated version.

By investing time and effort in creating a comprehensive sales process flowchart, small businesses can enhance sales efficiency, streamline operations, and drive better results across the sales pipeline.
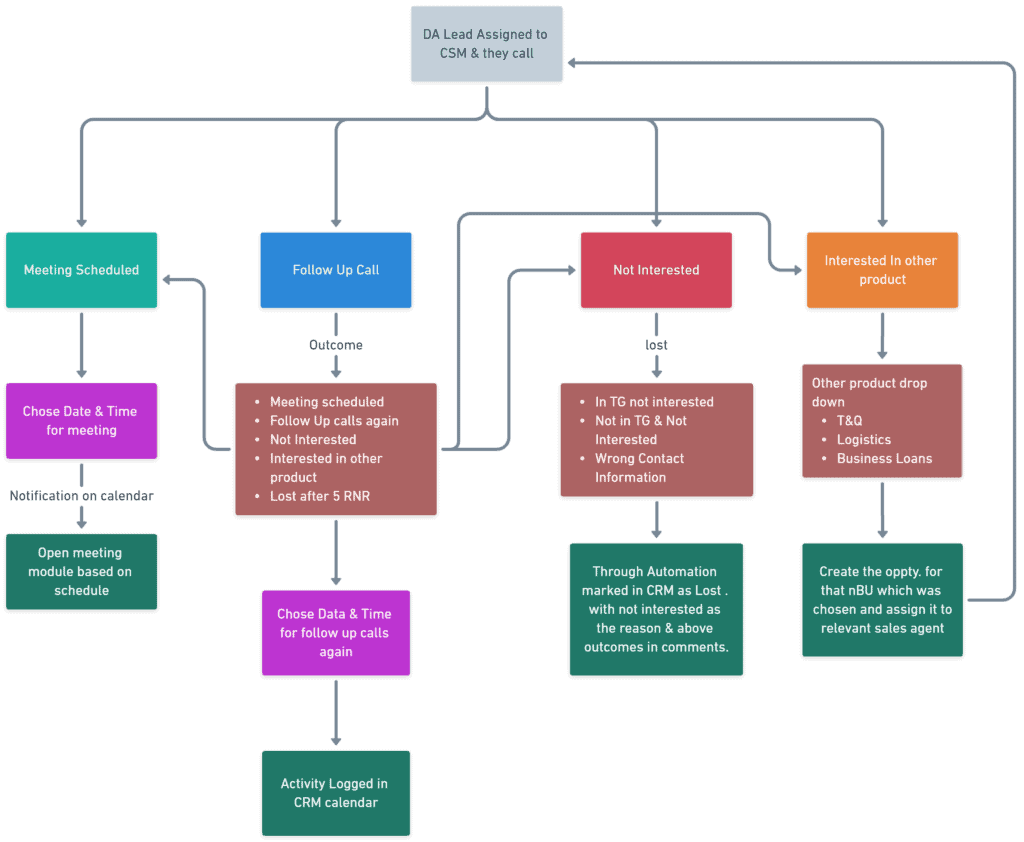
Identify Prospects (Potential Customers): This is the initial stage where potential customers are identified through various methods such as marketing campaigns, referrals, or networking.
Qualify Leads (Lead Generation): Once prospects are identified, they are qualified based on criteria such as interest, budget, and fit with the products or services offered.
Present Solutions (Product/Service): Qualified leads are presented with solutions that address their needs and pain points. This stage involves product demonstrations, proposals, and showcasing the value proposition.
Negotiate Terms (Pricing, Contracts): Negotiations take place regarding pricing, terms, and conditions. This stage involves reaching mutually beneficial agreements and finalizing contracts.
Close Deals (Sales Conversion): The successful completion of negotiations leads to closing deals and converting prospects into paying customers.
Follow-Up & Support (Customer Relations): After the sale is made, ongoing support, follow-up, and customer relations efforts are crucial for building long-term relationships and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Real-Life Example: Implementing a Sales Process for a Small Business

Let’s delve into a the process that i implemented at ‘nexarc’ to illustrate how a small business can implement a structured sales process effectively. ‘nexarc’ specialized in a custom software solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises called ‘nexGrow’ which helped small businesses generate leads.
Initial Prospecting and Lead Generation: Nexarc employs various lead generation strategies such as content marketing, social media outreach, and targeted advertising to attract potential leads interested in optimizing their lead generation efforts.
The marketing team utilizes NexGrow’s features to showcase its effectiveness in generating quality leads.
Qualifying Leads and Needs Assessment: As leads come in, Nexarc’s sales team qualifies them based on factors like industry, company size, and lead generation challenges.
A sales rep conducts a detailed needs assessment with each qualified lead to understand their specific requirements, pain points, and customization preferences for NexGrow.Example: One of Nexarc’s leads is a B2B software company looking to boost lead quality and conversion rates through personalized lead generation strategies tailored to different buyer personas.
Presenting Tailored Solutions: Armed with insights from the needs assessment, Nexarc presents a tailored solution proposal using NexGrow. The proposal outlines how NexGrow can be customized to capture and nurture leads effectively, showcasing its features such as lead scoring, automated follow-ups, and A/B testing capabilities.
Example: Nexarc demonstrates how NexGrow can integrate with the B2B software company’s CRM system, segment leads based on behavior, and deliver personalized content to enhance engagement and conversions.
Negotiating and Finalizing Terms: Nexarc engages in negotiations with the B2B software company, discussing pricing tiers based on the level of customization and support required. The sales rep collaborates with Nexarc’s product development team to ensure NexGrow can deliver on the promised customization and functionality.
Example: After negotiations, Nexarc and the B2B software company agree on a pricing structure that includes initial setup costs, monthly subscription fees, and optional add-on features for advanced lead management.
Closing the Deal and Onboarding: With terms finalized, Nexarc closes the deal with the B2B software company and initiates the onboarding process for NexGrow. Nexarc’s onboarding team works closely with the client to configure NexGrow according to their specifications, import existing leads data, and conduct training sessions for their team.
Example: The B2B software company officially signs the contract with Nexarc, and NexGrow is customized to align with their lead generation objectives. Nexarc provides ongoing support and troubleshooting during the onboarding phase to ensure a smooth transition.
Post-Sale Support and Relationship Building: Nexarc continues to support the B2B software company post-launch, offering regular check-ins, performance reviews, and feature updates for NexGrow. Nexarc’s customer success team collaborates with the client to optimize their lead generation strategies and maximize the ROI from NexGrow.
Example: Nexarc conducts quarterly performance reviews with the B2B software company, analyzing lead generation metrics, identifying areas for improvement, and suggesting new features or integrations to enhance NexGrow’s functionality.
Exploring the Seven Essential Steps of the Sales Process
Managing the sales process effectively is paramount for small businesses to drive revenue growth and build lasting customer relationships. Let’s go deeper into the seven essential steps that form the backbone of a successful sales process:
Prospecting and Lead Generation (Identify Prospects)
The journey begins with prospecting and lead generation, where sales reps identify potential customers or leads who could benefit from their products or services.
This involves leveraging marketing campaigns, networking events, referrals, and digital channels to create a pipeline of qualified leads for further engagement.
Qualifying Leads (Lead Qualification)
Once leads are identified, the next step is to qualify them based on predefined criteria such as budget, timeline, decision-making authority, and fit with the company’s offerings.
Qualifying leads ensures that sales teams prioritize their efforts on prospects with the highest potential for conversion.
Needs Assessment and Solution Presentation (Present Solutions)
A crucial aspect of the sales process is conducting a thorough needs assessment with qualified leads. This involves understanding their pain points, challenges, goals, and specific requirements.
Based on the needs assessment, sales reps tailor solution presentations that highlight how their products or services can address the prospect’s needs effectively.
Handling Objections and Negotiating Terms (Negotiate Terms)
During the sales interactions, prospects may raise objections or concerns regarding pricing, features, implementation, or competition. Effective sales reps anticipate objections and are equipped to address them confidently.
Negotiating terms involves finding common ground, showcasing value propositions, and reaching mutually beneficial agreements.
Closing the Deal (Close Deals)
The pinnacle of the sales process is closing the deal and converting prospects into paying customers.
This involves securing commitments, finalizing contracts, and ensuring a smooth transition from the sales stage to the implementation or delivery phase.
Post-Sale Support and Relationship Building (Follow-Up & Support)
The sales process extends beyond the initial transaction, focusing on post-sale support and relationship building.
Sales teams provide ongoing support, address customer inquiries or issues, and nurture relationships to foster loyalty, repeat business, and referrals.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback (Review and Refine)
A key aspect of a successful sales process is continuous improvement based on feedback and performance metrics.
Sales teams review outcomes, gather customer feedback, analyze conversion rates, and refine strategies or tactics to enhance sales effectiveness and optimize results.
Defining the Sales Process Stages for Small Business Owners
Lets look at defining the sales process stages from perspectives on the impact of each stage on the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement for you as a small business owner:
Prospecting and Lead Generation:
Impact on P&L: Lead generation directly affects marketing expenses. As a small business owner, I’ve learned that investing in targeted lead generation strategies yields better results than generic mass marketing. By focusing on quality leads, even if the initial cost is slightly higher, the long-term impact on revenue and profitability is significant.
Qualifying Leads:
Impact on P&L: Qualifying leads efficiently is crucial for cost-effective sales efforts. In my experience, dedicating time to thoroughly qualify leads has resulted in higher conversion rates and reduced acquisition costs. It’s like sifting through gold nuggets from gravel – it requires effort but leads to better outcomes.
Needs Assessment and Solution Presentation:
Impact on P&L: Understanding customer needs and presenting tailored solutions is a delicate balance. I’ve found that aligning pricing with the perceived value of the solution, rather than simply competing on price, leads to healthier margins and satisfied customers who are willing to pay for value.
Handling Objections and Negotiating Terms:
Impact on P&L: Effective objection handling and negotiation skills are paramount. I recall a situation where a customer raised concerns about pricing, but by highlighting the unique benefits and ROI of our solution, we were able to justify the price and maintain margins without compromising on value.
Closing the Deal:
Impact on P&L: Closing deals is exhilarating yet critical for revenue growth. I’ve seen firsthand how a well-timed and professionally executed closing can lead to not just immediate revenue but also long-term customer loyalty and additional business opportunities.
Post-Sale Support and Relationship Building:
Impact on P&L: Post-sale support is where customer retention and referrals thrive. I’ve witnessed the power of building strong relationships with clients post-sale – it not only reduces churn and acquisition costs but also opens doors to upselling and cross-selling opportunities.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback:
Impact on P&L: Continuously improving based on feedback is a game-changer. Incorporating customer feedback into product/service enhancements not only boosts customer satisfaction but also strengthens brand loyalty, leading to higher lifetime customer value and sustainable revenue streams.
The Role of Sales Reps in Executing the Sales Process
Like any process, if your sales process has to be successful, your salesteam should be actively involved in deciding the factors that play an important role for the customer
Involvement in Creating the Sales Process: Sales reps play a vital role in shaping the sales process due to their frontline experience and direct interactions with prospects and customers. When designing or refining the sales process, involving sales reps ensures practicality, alignment with customer needs, and buy-in from the team.
Sharing Findings from Customer Interactions: Sales reps gather invaluable insights from customer interactions, including pain points, objections, buying motivations, and market trends. Sharing these findings with the sales team and other relevant departments such as marketing and product development informs strategy adjustments, product/service enhancements, and targeted messaging.
Getting Sales Reps Buy-In: Achieving buy-in from sales reps is essential for sales process adherence and effectiveness. Here are key strategies to garner sales reps’ buy-in:
- Communication and Collaboration: Involve sales reps in sales process discussions, seek their input, and explain the rationale behind process changes or updates. Collaborative decision-making fosters ownership and commitment.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training on the sales process, tools, and techniques. Address any skill gaps and offer ongoing support to ensure sales reps feel equipped and confident in executing the process.
- Highlight Success Stories: Share success stories and case studies that demonstrate how following the sales process has led to successful deals, satisfied customers, and personal career growth for sales reps. Positive reinforcement reinforces the value of adherence.
- Feedback Loop: Create a feedback loop where sales reps can provide input, share challenges, and suggest improvements to the sales process. Actively listen to their feedback, implement feasible suggestions, and acknowledge their contributions.
- Recognition and Rewards: Recognize and reward sales reps who consistently demonstrate sales process adherence, achieve targets, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. Incentives, recognition programs, and career advancement opportunities motivate buy-in and performance.
Creating an Effective Sales Process Structure for Your Business
Creating an effective sales process structure for your business requires careful planning, strategic thinking, and thorough preparation. Here’s a detailed guide on the prep work that small business owners need to do and some brainstorming topics they can incorporate to build a successful sales process:
Prep Work for Creating an Effective Sales Process:
- Define Your Target Audience: Clearly identify your ideal customer profile (ICP) by considering demographics, industry, pain points, buying behavior, and preferences. Understanding your target audience is fundamental to crafting a tailored sales process.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define specific sales goals, targets, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your business objectives. Whether it’s revenue targets, customer acquisition rates, or conversion rates, clarity on objectives guides the sales process design.
- Map Out Customer Journey: Visualize the typical customer journey from awareness to purchase and post-sale interactions. Identify touchpoints, decision-making stages, and potential barriers or objections along the way to streamline the sales process.
- Identify Sales Funnel Stages: Define stages of your sales funnel such as prospecting, lead qualification, needs assessment, proposal, negotiation, closing, and post-sale support. Each stage should have clear objectives, actions, and success criteria.
- Develop Buyer Personas: Create detailed buyer personas representing different customer segments within your target audience. Dive deep into their needs, motivations, challenges, goals, objections, and preferred communication channels.
- Map Sales Process Steps: Outline the specific steps, actions, and interactions involved in each sales stage. Consider incorporating sales methodologies or frameworks like SPIN Selling, Challenger Sale, or consultative selling techniques based on your business needs.
- Define Sales Collateral and Tools: Determine the necessary sales collateral, tools, and technology stack to support the sales process. This may include CRM software, sales decks, product demos, case studies, pricing sheets, and proposal templates.
- Establish Sales Metrics and Reporting: Define key metrics to track sales performance, such as conversion rates, pipeline velocity, win rates, average deal size, and customer lifetime value (CLV). Implement a robust reporting system to monitor progress and make data-driven decisions.
Brainstorming Topics for Small Business Owners which can be used as a part of the sales process creation exercise
- Value Proposition Refinement
- Objection Handling Strategies
- Customer Engagement Ideas
- Sales Training and Development
- Cross-Selling and Upselling Opportunities
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Leveraging Technology in Streamlining Your Sales Process
Leveraging technology is essential for streamlining the sales process in today’s digital age. Small business owners can benefit from CRM software (Customer Relationship Management) to track leads, manage customer interactions, and automate follow-ups.
Additionally, sales enablement tools like sales engagement platforms, email marketing software, and analytics tools provide valuable insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and business trends.
Integration with communication tools such as video conferencing platforms and messaging apps facilitates seamless communication with prospects and sales teams, enhancing collaboration and efficiency.
Nurturing Prospects: The Heart of the Sales Cycle

Nurturing potential customers for small businesses goes beyond generic marketing approaches. It’s about diving deep into customer pain points, understanding their needs, and crafting tailored messages that resonate.
Rather than relying solely on traditional advertising, successful nurturing involves building authentic connections through digital channels like social media, email marketing, and content creation.
One key aspect is aligning your brand narrative with what matters most to your target audience. This means highlighting how your product or service solves their specific challenges or improves their lives.
By focusing on storytelling that speaks directly to customer emotions and aspirations, you can create a lasting impression and build trust.
Additionally, nurturing involves continuous engagement and relationship-building. This includes regular communication through personalized emails, social media interactions, and valuable content such as blog posts or videos.
By staying top-of-mind and providing consistent value, you can nurture leads from initial interest to eventual conversion.
Moreover, leveraging data and analytics plays a crucial role in effective nurturing. Tracking customer interactions, preferences, and behaviors allows you to tailor your approach, send relevant messages at the right time, and identify opportunities for further engagement.
In essence, successful nurturing for small businesses is about delivering targeted, meaningful experiences that address customer needs, foster trust, and ultimately drive long-term loyalty and growth.
Crafting a Compelling Sales Pitch for Small Business Owners

A good sales pitch is crucial for small businesses looking to boost sales effectively. It’s a presentation or conversation with potential customers where you articulate the value of your solution, addressing their biggest problem in a particular aspect of their lives. Crafting a compelling sales pitch involves several key steps:
- Identify Customer Pain Points: Understand your customers’ challenges deeply to tailor your pitch effectively.
- Highlight Solutions: Present your solution early in the conversation to set high expectations and demonstrate how it comprehensively solves their problem.
- Stand Out from Competition: Showcase what makes your business unique and why your solution is superior to alternatives in the market.
- Provide Social Proof: Share success stories or testimonials from satisfied customers to build trust and credibility.
- Engage with Interactive Elements: Incorporate visuals, demonstrations, or case studies to engage customers and make your pitch more memorable.
- Call to Action: Encourage customers to take the next step, whether it’s scheduling a follow-up meeting, signing up for a trial, or joining your community.
Additionally, small business owners should invest in training their sales teams, understanding customer objections, and structuring their pitches strategically to maximize impact.
Building a sales pitch around storytelling, customer empathy, and clear value propositions can significantly enhance sales conversions and long-term customer relationships.
For all the details, refer my article linked above so that you can spend a good 15 minutes to learn the essentials of a great sales pitch.
Identifying and Qualifying Sales Leads in Your Sales Process
In the quest to identify target customers for a small business, understanding your market and audience is crucial. Think of it as creating a recipe where each ingredient plays a vital role in the final dish—your success.
To start, delve deep into your customers’ pain points. It’s like being a detective, uncovering clues to solve a mystery.
Ask yourself: What exact problem does my product or service solve? How significant is this problem for my customers? Does my solution offer a substantial improvement for them? And most importantly, can I find a substantial number of customers who resonate with this pain point?
This process isn’t just about throwing darts in the dark; it’s about precision targeting. Imagine you’re an archer aiming for the bullseye, not just any spot on the target.
Once you’ve pinpointed your ideal customer, it’s time to craft your message. Think of it as tailoring a suit—you want it to fit perfectly. Understand your customer’s preferences, interests, and demographics.
Don’t just stop at surface-level data; dive deep into their world.
Now, let’s talk strategy. It’s like playing chess; you need to think several moves ahead. Utilize multiple marketing channels like content marketing, influencer marketing, and email campaigns.
It’s akin to having an orchestra where each instrument plays its part harmoniously. Remember, data is your best friend. Collect as much relevant data as you can about your customers. It’s like having a treasure map that leads you to hidden riches.
Lastly, adaptability is key. It’s like being a chameleon, changing colors to blend seamlessly with your environment. Monitor and adjust your strategies based on real-time feedback. Think of it as fine-tuning a musical instrument; small tweaks can create beautiful melodies.
Basically, identifying and qualifying sales leads is a symphony of understanding your market, targeting the right audience, crafting compelling messages, leveraging data, and staying flexible in your approach. .
Integrating Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Your Sales Process

To explain this in detail, i will walk you through an example of a friend’s boutique where she did the following things to integrate her CRM with her sales process. I have changed the name of her store for privacy reasons.
1. Customer Data Organization:
- All Good Things Clothing Boutique organized customer data effectively within the CRM. This included capturing essential information like customer contact details, purchase history, preferences, and communication preferences.
- The business owner ensured that the CRM was configured to categorize customers based on factors such as buying frequency, average purchase value, and loyalty status. This segmentation allowed for targeted marketing and personalized sales efforts.
2. Lead Management:
- CRM tools were utilized to track and manage leads efficiently. Leads were captured from various sources such as website inquiries, social media engagement, and offline events.
- Lead scoring mechanisms were implemented within the CRM to prioritize leads based on factors like engagement level, buying intent, and fit with ideal customer profiles. This helped sales teams focus on high-potential leads for better conversion rates.
3. Sales Pipeline Visibility:
- The CRM provided clear visibility into the sales pipeline, from lead generation to closing deals. Pipeline stages were customized to reflect the specific sales process of All Good Things Clothing Boutique, including prospecting, qualification, proposal, negotiation, and closing.
- Sales reps could easily track the progress of deals, identify bottlenecks, and prioritize activities to move deals forward effectively.
- Sales managers could drive weekly sales meetings with enough data and rigour to avoid missing out on any prospects
4. Task and Activity Management:
- CRM features for task and activity management were leveraged. Tasks were assigned to sales team members, deadlines were set, and progress was tracked within the CRM platform.
- Regular updates and documentation of customer interactions, meetings, follow-ups, and sales activities were encouraged, ensuring that everyone in the team was aligned and informed about ongoing sales efforts.
5. Customer Communication and Engagement:
- CRM capabilities were used to streamline customer communication and engagement. Email automation, personalized messaging, and follow-up reminders were implemented to maintain consistent and meaningful interactions with customers.
- Omnichannel communication within the CRM was enabled, allowing sales reps to connect with customers via email, phone calls, social media, and other channels from a centralized platform.
6. Data Analysis and Reporting:
- CRM analytics and reporting tools were leveraged to gain insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and trends. Customized reports and dashboards were generated to monitor key metrics such as conversion rates, sales cycle length, customer retention, and revenue growth.
- Data-driven insights were used to identify opportunities for improvement, refine sales strategies, and make informed business decisions.
Through the implementation of these CRM parameters, All Good Things Clothing Boutique improved efficiency, built better customer relationships, and increased sales revenue.
Strategies for Closing Sales Deals in the Small Business Context
Closing sales deals isn’t just about transactions; it’s about crafting narratives that resonate deeply with customers. Imagine your business as a storyteller, each interaction a chapter in a compelling tale of value and connection.
Here’s how you can infuse the art of storytelling into your sales strategy to effectively close deals. You can also read about it in detail and borrow my framework for telling compelling stories that will help you close deals.
Begin by setting the stage with a warm welcome and genuine interest in your customer’s needs. Much like a protagonist stepping into an adventure, your customer should feel valued and understood from the very start. Create an atmosphere where every product or service becomes a character in their unique story, addressing their pain points and aspirations.
As the story unfolds, weave in the emotional journey – the struggle, the tension, and the desire for resolution. Highlight how your offerings can be the hero that helps overcome challenges and achieve goals. Use testimonials or case studies as plot twists, showcasing real-life triumphs that resonate with your customer’s experiences.
In the climax, don’t just present a product or service; offer a solution that transforms their narrative. Emphasize the benefits and outcomes, painting a vivid picture of success and satisfaction.
Make them envision themselves as the protagonist of a story where your business plays a pivotal role in their journey towards success.
Finally, close the deal by reinforcing the emotional connection and the value proposition. Offer personalized incentives or bonuses that add an extra layer of excitement to their narrative.
Leave them feeling empowered and eager to embark on the next chapter with your business as their trusted ally.
By embracing storytelling in your sales process, you create memorable experiences that go beyond mere transactions. You build lasting relationships, foster loyalty, and turn customers into advocates who eagerly share their positive experiences with others.
Remember, every sale is not just a transaction; it’s a chapter in a story of growth, success, and partnership.
Continuous Improvement: Monitoring and Optimizing Your Sales Process
Here are 10 good practices which any business owner should implement as a part of their sales process improvement initiatives.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your sales process to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement. Analyze key metrics such as conversion rates, lead-to-customer ratios, and sales cycle length to track performance over time.
- Customer Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops with customers to gather insights into their experience with your sales process. Use surveys, interviews, and customer reviews to understand pain points, preferences, and areas where the process can be enhanced.
- Sales Team Training: Invest in ongoing training and development for your sales team. Provide resources and tools to improve their sales skills, product knowledge, and customer relationship management. Encourage continuous learning and adaptation to evolving market trends.
- Utilize CRM Data: Leverage data from your customer relationship management (CRM) system to track sales activities, customer interactions, and sales pipeline progress. Analyze trends, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to optimize the sales process.
- Implement Sales Automation: Explore sales automation tools and software to streamline repetitive tasks, automate follow-ups, and improve efficiency. This can free up time for your sales team to focus on high-value activities and strategic relationship-building.
- Regular Process Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your sales process to identify inefficiencies, roadblocks, and opportunities for optimization. Collaborate with sales team members to gather input and ideas for process improvements.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Benchmark your sales process against industry standards and competitors. Identify best practices, trends, and innovations that can inspire improvements and differentiation in your approach.
- Continuous Experimentation: Encourage a culture of experimentation and innovation within your sales team. Test new sales strategies, messaging techniques, and outreach methods to identify what resonates best with your target audience.
- Feedback from Sales Team: Solicit feedback from your sales team on their experience with the sales process. Gather insights into challenges they face, tools they find effective, and areas where additional support or resources are needed.
- Iterative Improvements: Embrace an iterative approach to sales process improvement. Implement changes, measure their impact, gather feedback, and iterate further based on results. Continuous improvement is an ongoing journey of refinement and adaptation to meet evolving customer needs and market dynamics.
With this i believe that you are now positioned to implement a robust sales process for your business.
